Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, businesses are constantly faced with the challenge of staying relevant and competitive. One of the key areas that organizations need to address is the modernization of their legacy systems. Legacy systems, which are outdated and often no longer supported by vendors, can hinder innovation, efficiency, and growth. This is where solution architecture plays a crucial role in enabling successful legacy system modernization.
The Importance of Enterprise Architecture
What is Enterprise Architecture?
Enterprise Architecture (EA) is a strategic framework that helps organizations align their business processes, information systems, and technology infrastructure with their overall goals and objectives. It provides a holistic view of an organization's current state and desired future state, allowing decision-makers to make informed choices about technology investments and transformations.
How Does Enterprise Architecture Help in Legacy System Modernization?
Enterprise Architecture serves as a guide for legacy system modernization initiatives by providing a structured approach to understanding the organization's IT landscape. It helps identify areas where improvements are needed and defines the target architecture that supports the organization's goals.
Enterprise Architecture tools play a critical role in this process by providing capabilities for documenting current systems, analyzing dependencies, and creating roadmaps for migration or transformation. These tools enable architects to visualize complex IT landscapes, assess risks associated with legacy systems, and model future-state architectures.
The Role of Solution Architecture
What is Solution Architecture?
Solution Architecture focuses on designing specific solutions that address business requirements within the broader enterprise architecture context. It involves defining the structure, behavior, and integration of individual components or modules that make up a larger system.
How Does Solution Architecture Support Legacy System Modernization?
When it comes to legacy system modernization, solution architecture plays a vital role in ensuring the successful transformation of outdated systems into modernized ones. Here are some key ways in which solution architecture contributes:
Assessment of Legacy Systems: Solution architects assess the existing legacy systems to understand their strengths, weaknesses, and dependencies. They identify the areas that need improvement or replacement and propose suitable solutions.
Designing Target Architectures: Solution architects work closely with enterprise architects to define target architectures that align with the organization's goals and objectives. They ensure that the new system integrates seamlessly into the existing IT landscape.
Vendor Evaluation and Selection: Solution architects evaluate potential vendors and products that can support the modernization initiative. They assess factors such as compatibility, scalability, security, and cost-effectiveness to make informed decisions.
Defining Migration Strategies: Solution architects develop migration strategies that outline the steps and processes required to transition from legacy systems to modernized ones. They consider factors such as data migration, integration challenges, and user training.
Collaboration with Development Teams: Solution architects collaborate closely with development teams to ensure that the designed solutions are implemented effectively. They provide guidance on best practices, design patterns, and architectural standards.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Solution architects identify potential risks associated with legacy system modernization and develop strategies to mitigate them. This includes assessing impacts on business operations, data integrity, security, and compliance.
Solution Architecture Management
The Role of a Solution Architect
A Solution Architect is responsible for driving the design and implementation of solutions that meet specific business requirements within the broader enterprise architecture framework. They possess a deep understanding of technology trends, industry best practices, and architectural principles.
Key Responsibilities of a Solution Architect
Requirement Analysis: Solution architects analyze business requirements and translate them into technical specifications. They identify gaps in existing systems and propose suitable solutions.
Solution Design: Solution architects design scalable, secure, and robust solutions that address business needs. They consider factors such as performance, scalability, reliability, availability, maintainability, and usability.
Collaboration with Stakeholders: Solution architects work closely with stakeholders, including business users, project managers, and development teams. They ensure that the designed solutions align with business goals and objectives.
Technical Leadership: Solution architects provide technical leadership to development teams, guiding them on architectural standards, design patterns, and best practices. They also conduct code reviews and ensure compliance with architectural guidelines.
Continuous Improvement: Solution architects continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of implemented solutions. They identify areas for improvement and propose enhancements to optimize system performance and reliability.
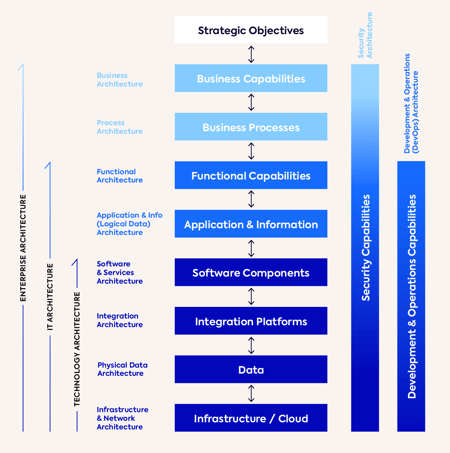
The Role of Enterprise Architecture Tools in Solution Architecture Management
Enterprise Architecture tools play a crucial role in solution architecture management by providing capabilities for documenting, modeling, and analyzing architectures. These tools enable solution architects to:
Visualize Architectures: Enterprise Architecture tools allow solution architects to create visual representations of architectures, making it easier to communicate complex ideas to stakeholders.
Capture Requirements: These tools provide features for capturing and managing business requirements. Solution architects can link requirements to specific components or modules within the overall architecture.
Modeling Solutions: Enterprise Architecture tools support modeling capabilities that enable solution architects to design detailed solutions, considering factors such as data flows, integration points, and user interfaces.
Impact Analysis: Solution architects can use enterprise architecture tools to perform impact analysis on proposed changes or enhancements. This helps them understand the potential impacts on other components or systems.
Collaboration and Documentation: Enterprise Architecture tools facilitate collaboration among solution architects, stakeholders, and development teams. They provide a central repository for documentation, ensuring that all relevant information is easily accessible.
Application Portfolio Management (APM) for Legacy System Modernization
What is Application Portfolio Management (APM)?
Application Portfolio Management (APM) is a practice that helps organizations assess their application landscape, rationalize applications based on business value, and make informed decisions about modernization, consolidation, or retirement.
The Role of APM in Legacy System Modernization
APM plays a crucial role in legacy system modernization by providing a structured approach to managing and optimizing the application portfolio. Here's how APM supports the modernization process:
Inventory and Assessment: APM tools, such as ServiceNow Application Portfolio Management (APM) tools, enable organizations to inventory their applications, capturing key information such as technology stack, dependencies, usage patterns, and business value.
Identification of Modernization Candidates: APM helps identify legacy applications that are prime candidates for modernization based on factors such as outdated technology, high maintenance costs, security vulnerabilities, or lack of scalability.
Rationalization and Prioritization: APM tools provide capabilities for evaluating applications based on their business value, technical health, and alignment with strategic objectives. This helps organizations prioritize modernization efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Roadmap Planning: APM facilitates the creation of roadmaps for application modernization by considering factors such as dependencies, risks, budgets, and timelines. It helps organizations plan phased migration strategies to minimize disruption to business operations.
Tracking and Monitoring: APM tools enable organizations to track the progress of modernization initiatives and monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cost savings, improved efficiency, and enhanced user satisfaction.
FAQs
Q: What are the main challenges associated with legacy system modernization? A: Legacy system modernization can be challenging due to factors such as complex interdependencies among systems, data migration issues, compatibility concerns with existing infrastructure, resistance to change from end-users, and budget constraints.
Q: How long does it take to complete a legacy system modernization project? A: The duration of a legacy system Extra resources modernization project depends on various factors including the size and complexity of the system, the availability of resources, and the scope of the modernization effort. It can range from several months to a few years.
Q: What are some common approaches to legacy system modernization? A: Common approaches to legacy system modernization include rehosting (migrating to a new infrastructure without significant changes), re-platforming (migrating to a new technology platform), replacing (developing or purchasing a new system), and retiring (phasing out the legacy system).
Q: How can solution architecture mitigate risks associated with legacy system modernization? A: Solution architecture helps mitigate risks associated with legacy system modernization by conducting thorough assessments, defining robust target architectures, and developing migration strategies. It ensures that potential risks such as data loss, security breaches, and operational disruptions are identified and addressed proactively.
Q: What role does user training play in legacy system modernization? A: User training is crucial in legacy system modernization as it helps end-users adapt to the changes introduced by the new system. Training programs ensure that users understand how to effectively utilize the new features and functionalities, minimizing productivity losses during the transition period.
Q: How can organizations measure the success of their legacy system modernization initiatives? A: Organizations can measure the success of their legacy system modernization initiatives through key performance indicators (KPIs) such as improved system performance, reduced maintenance costs, increased user satisfaction, enhanced data quality, and streamlined business processes.
Conclusion
Legacy system modernization is a critical endeavor for organizations seeking to stay competitive in today's fast-paced business environment. The role of solution architecture in this process cannot be underestimated. By leveraging enterprise architecture principles, solution architects help organizations assess their existing systems, design appropriate solutions, and manage the overall transformation journey. With the help of enterprise architecture tools and practices such as Application Portfolio Management (APM), organizations can streamline their modernization efforts, optimize their application landscape, and achieve their desired business outcomes.